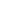Laboratory Emulsifier Purchasing Guide: Core Features, Applications, and Selection Recommendations
Release time:2025-12-09 Visits:557
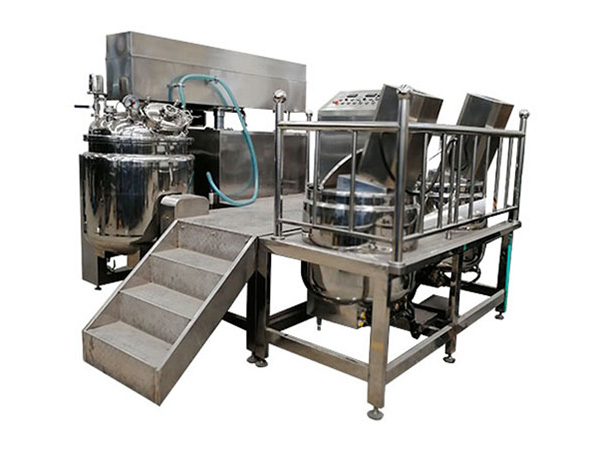
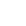
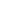
Laboratory emulsifiers are precision equipment designed specifically for small-batch material research and experimental purposes. They are widely used in performance verification of emulsified products such as creams, lotions, and emulsions, providing reliable data support for industrial production. Their core function is to achieve fine homogenization, dispersion, and emulsification of materials through high shear force, forming stable dispersion systems. This article will comprehensively introduce their core features, application fields, and key selection points to help you efficiently choose suitable equipment.
1. Core Features
The core features of
laboratory emulsifiers include flexible adaptability, high-performance parameters, material compatibility, and intelligent control.
1.1 Flexible Adaptability and Processing Capacity: Different models can be selected according to the experimental scale. Miniature emulsifiers are suitable for small-scale experiments of 10-500mL, reducing material waste; batch emulsifiers are suitable for medium batches of 500mL-5L; in continuous experiment scenarios, pipeline-type emulsifiers can be selected to adapt to continuous reaction systems. The working volume needs to match the experimental requirements, for example, a common model has a designed volume of 6L and an actual working volume of 5L.
1.2 Key Performance Parameters: The speed range is usually 1000–10000rpm, nano-level emulsification requires above 20000rpm, and some models support stepless speed regulation from 1000–14000rpm. The shearing capacity adopts a claw-type, achieving bidirectional material suction, avoiding dead corners, and the rotor linear speed can reach 20.5m/s, ensuring efficient shearing. In terms of power configuration, the homogenizing motor power is usually 0.55kW (batch type) to 500W (miniature), and the dispersing motor power is approximately 0.55kW, supporting high-torque processing of high-viscosity materials.
1.3 Material Property Adaptation: High-viscosity materials require a scraper stirring system (power 0.55kW, speed 0–100rpm) to achieve全方位 wall scraping and ensure no residue. Heat-sensitive materials need an integrated temperature control system, supporting jacket cooling or heating with a temperature control range of -5~100℃. For foamy or aseptic operation scenarios, vacuum emulsifier models should be selected, made of 316L stainless steel and supporting high-temperature sterilization (121℃).
1.4 Intelligent and Safety Control: Advanced models are equipped with intelligent control systems, supporting touch screen display of real-time parameters (such as voltage, current, power, torque curve), and featuring overload protection, leakage protection, and automatic shutdown function when the cover is opened. Programmed control can store multiple sets of parameters, improving experimental repeatability and operational safety.
2. Application Fields
Laboratory emulsifiers are suitable for multiple industries, including:
- Biopharmaceuticals: Used for tissue homogenization, enzyme preparations, and aseptic preparation of medical emulsions.
- Cosmetics: Supporting formula development of creams, serums, and lotions.
- Food Industry: Used for homogenization of fruit juices, dairy products, and sauces.
- Chemical Materials: Applied in scenarios such as nanomaterial dispersion, lubricating oil, and pesticide emulsification. Their small size, portability, and easy operation efficiently support process verification and optimization in the R&D stage.
3. Selection Recommendations
When selecting a model, the following factors should be comprehensively considered:
- Processing Capacity: Choose a suitable volume according to the single experiment scale to avoid resource waste.
- Material Properties: High-viscosity materials require a reinforced stirring system, and heat-sensitive materials require precise temperature control.
- Functional Requirements: Aseptic operations require vacuum and 316L material, while continuous experiments require a pipeline-type structure.
- Data Recording: For R&D scenarios, it is recommended to select models with online monitoring (such as temperature, viscosity, particle size) and data export functions to ensure experimental repeatability and accuracy.
In conclusion, laboratory emulsifiers, with their precision, flexibility, and efficiency, have become indispensable equipment in the R&D process. Through reasonable selection, experimental efficiency and data reliability can be significantly improved, laying a solid foundation for industrial production.