Comprehensive Analysis of Homogenizing Emulsifier: From Core Mechanism to Industry Selection Guide
Release time:2025-12-09 Visits:322
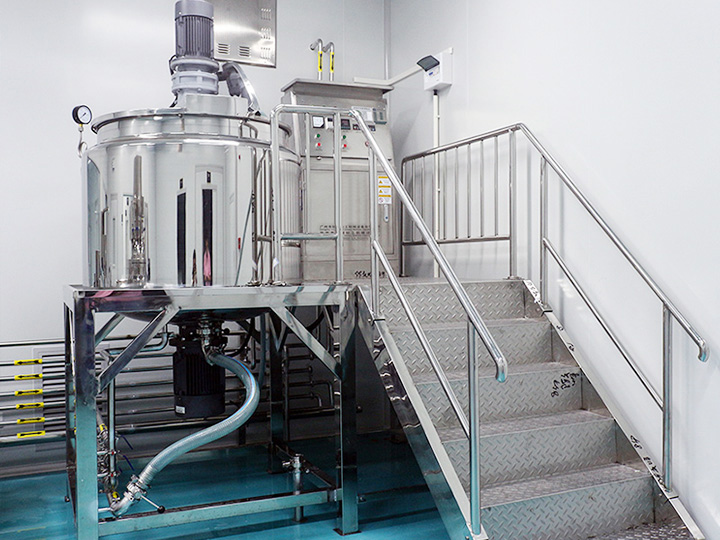
A homogenizing emulsifier is a key equipment that uniformly disperses immiscible liquids or solid particles through high-intensity mechanical action to form stable emulsions or suspensions. Its core value lies in significantly improving product stability, uniformity, and user experience, with wide applications in cosmetics, food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries.
1. Core Working Principle: Multi-Mechanical Synergy
Homogenizing
emulsifiers achieve ultra-fine dispersion of materials through the following mechanisms:
1. High-Intensity Shearing
The high-speed rotating rotor and precision stator form micron-level gaps. When materials pass through, they undergo intense shearing forces, breaking large particles into micron/nano-sized particles.
2. Cavitation Effect
Rapid pressure drop during high-speed flow causes liquid vaporization to form bubbles. The collapse of bubbles generates local high-pressure shock waves (up to 1000 atmospheres), further breaking particles.
3. Turbulent Impact
Materials impact the inner wall of the homogenizing valve or other streams at extremely high speeds, achieving particle depolymerization through collision force. Multistage circulation processing ensures uniform particle size distribution.
2. Equipment Types and Applicable Scenarios
1. High-Speed Shear Homogenizer
• Features: Rotor-stator structure, suitable for small to medium batch production
• Advantages: Flexible operation, easy cleaning, low cost
• Applications: Laboratory research, cosmetic emulsions, sauce pretreatment
2. High-Pressure Homogenizer
• Features: Uses 100-2000bar high-pressure jet crushing
• Advantages: Precise particle size control (up to nanoscale), high processing efficiency
• Applications: Dairy homogenization, injection emulsification, high-end nanomaterial dispersion
3. Vacuum Homogenizing System
• Features: Closed environment with degassing function
• Advantages: Prevents bubble incorporation and oxidative deterioration
• Applications: High-end creams, ointments, oxygen-sensitive products
3. In-Depth Industry Application Analysis
1. Cosmetics Industry
Achieves uniform distribution of active ingredients during the production of emulsions and serums, enhancing product skin feel and stability while preventing stratification and precipitation.
2. Food and Beverage
• Dairy Products: Breaks fat globules to prevent floating and extend shelf life
• Fruit Juices: Refines pulp fibers to improve taste
• Sauces: Maintains emulsion system to avoid oil-water separation
3. Pharmaceutical Field
Ensures uniform drug distribution when preparing liposomes and emulsion injections, guaranteeing accurate dosage administration.
4. Chemical Industry
Used for pigment dispersion in coatings and inks, improving color uniformity and product stability.
4. Key Considerations for Selection
1. Material Properties: Viscosity, solid content, temperature sensitivity
2. Capacity Requirements: Laboratory type <50L/h, industrial grade up to 20T/h
3. Particle Size Requirements: 1-25μm for conventional applications, 0.1-1μm for high-end needs
4. Process Environment: Need for explosion-proof, sterile, or vacuum conditions
5. Equipment Compatibility: Matching with existing production line pipeline interfaces and control systems
5. Maintenance and Optimization Suggestions
• Regularly inspect rotor-stator gap wear
• Equip cooling systems for high-viscosity materials to control temperature
• Prioritize zirconia wear-resistant heads for hard particle materials
• Regularly verify particle size distribution to ensure optimal equipment performance